3 Emerging Technologies That Help Control Commercial Auto Risks
Common fleet auto risks, like reduced or sometimes lack of driver focus, qualification, training, and reinforcement of crucial defensive driving behaviors, can lead to devastating incidents when left unaddressed. New fleet technologies can help proactively manage drivers and simplify training opportunities, paving the way for safer roadways.
September 27, 2022

Screening criteria for your fleet drivers should be clearly defined in a written policy and acknowledged prior to hire as to what disqualifies an individual to drive on behalf of the employer. It can provide key details into their driving history, accidents, convictions, moving violations and suspensions. But new technologies can provide necessary insight into ongoing behaviors post-hire, where training may have lapsed, or safe driving practices have waned.
“Typically, drivers who have multiple violations are more likely to be involved in future accidents and should not be included as an acceptable fleet driver,” said Ariel Jenkins, Assistant Vice President – Risk Services at Safety National. “Technologies that run continuous monitoring can identify risky driving behavior like speeding, failure to obey traffic laws, and if a driver has a valid license for the types of vehicles they drive in the course of employment. They can reinforce behaviors to ensure that employees practice safe driving behaviors and remind drivers that their actions not only impact their employment, but also their lives and others’ lives on the road.”
These emerging technologies can help support your efforts to monitor and reach drivers.
1. Telematics
Telematics systems are becoming more widely available and utilized across multiple industries. These devices fit in a vehicle’s dashboard and combine navigation, safety and communication data. Fleet managers can benefit from their integration in several ways, including:
- Visibility – Provides organizations with vehicle GPS monitoring to track the movement or location of their fleet.
- Maintenance – Pulls engine data such as fuel consumption, temperature and engine load, which provides feedback to the management team, who can monitor and schedule regular vehicle maintenance.
- Safety – Provides insight into driving habits, so managers can create training programs or individual coaching sessions based on data, such as hard braking or aggressive acceleration.
- Cost savings – Fuel costs can be reduced through data that identify trends in driver behaviors, routes and maintenance that should be addressed.
- Compliance – Electronic and automatic drive time tracking make maintaining compliance on safety-related items much more manageable. Fleet managers can use telematics to track records of driver status, and certain providers can even streamline workflows associated with editing and certifying hours of service logs.
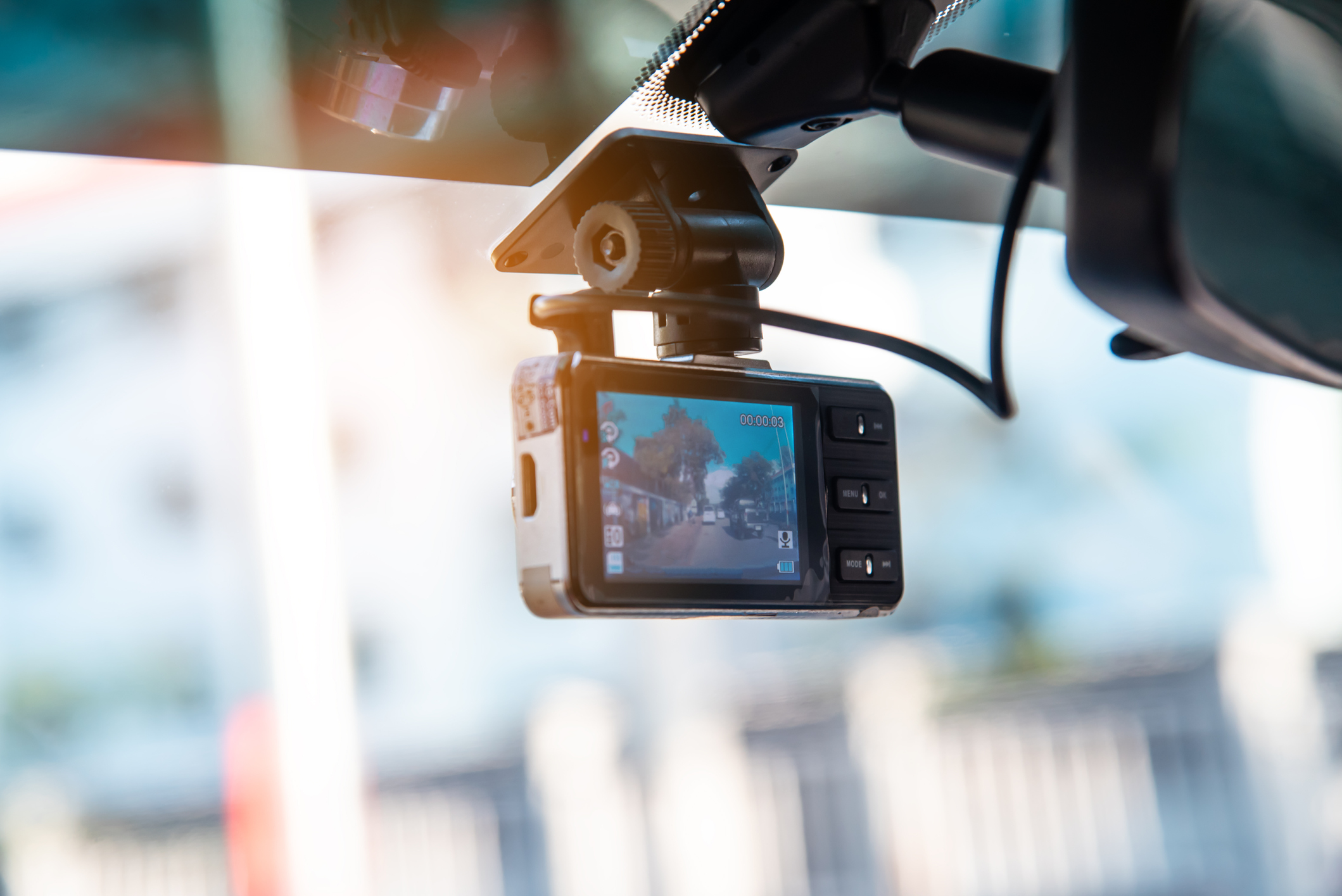
2. Smart Dash Cams
Dash cameras offer peace of mind by having the ability to record and review footage if an incident occurs. The footage can also be used to prove causation in a defense if a driver is involved in an accident. Some can even detect drowsiness, which can be considered impaired driving. Fleet managers can spot-check driver behavior by periodically reviewing footage of select drivers or drivers in question.
3. Motor Vehicle Record (MVR) Monitoring Systems
Electronic systems that can pull MVRs have continued to emerge throughout the last several years. With this continuous monitoring capability, if a “hit” is found on a driver’s MVR, an updated report is pulled and evaluated for accuracy. Employers are immediately alerted to any “hit” and receive the updated MVR for review. These could include accidents, DUIs, speeding tickets, or other motor vehicle violations or convictions.