How Telehealth’s Use Benefits Both Employers and Injured Workers
The adoption of telehealth in workers’ compensation is continually evolving, but its accessibility to care can remove treatment barriers limited by in-office visits. This ease of use can benefit both employer and employee.
February 13, 2024
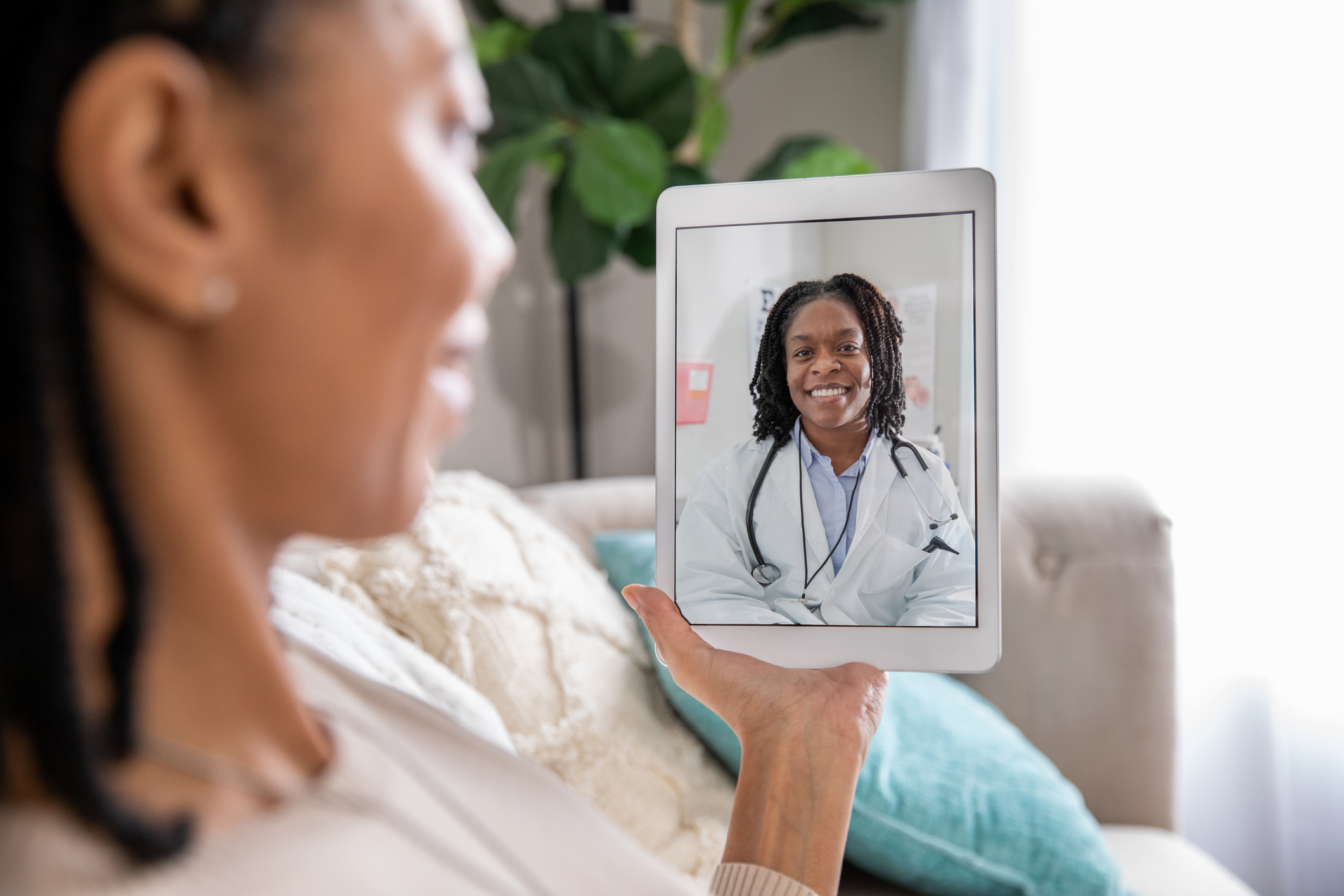

A recent report from the Workers’ Compensation Research Institute (WCRI) notes that although COVID-19 cases have declined, it is assumed that the utilization of telehealth, which was embraced during the height of the pandemic, will continue to remain significantly above pre-pandemic levels.
“Telehealth practices adopted for large healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, may very likely influence telehealth practices for the workers’ compensation industry,” said Anthony Bustillo, Vice President, Enterprise Risk Management and Chief Risk Officer at Safety National. “And while there are differences in state laws regarding the licensing of physicians, privacy policies, and prescribing guidelines, telehealth serves tremendous benefits, particularly for workers who previously had challenges interacting with the workers’ compensation system.”
Here, we outline the benefits of telehealth for employers and injured workers.
Benefits to Employers
Faster treatment times, reductions in emergency room (ER) visits, and quicker return to work serve to reduce overall claims costs, which ultimately benefits employers via lower premiums.
Self-insured employers may realize the benefits of telehealth even earlier, given the opportunity to promote the telehealth tools internally and to develop a physician network with extensive experience in treating the company’s most common injuries.
There can also be indirect financial benefits as injured workers may spend less time away from work traveling to and from doctor visits when used for follow-up appointments. However, this does create a responsibility for the employer to provide a location for the telehealth visit that ensures privacy.
Finally, there can be non-financial benefits to the employers due to the injured worker’s increased satisfaction with the process. With increased job satisfaction, an employer may have longer job tenure for its employees.
Benefits to Injured Workers
Faster access to diagnosis and treatment – Typically, the first and last appointment after an injury should be assessed in a healthcare facility to review an injured worker’s overall well-being and movement. However, depending on the injury’s severity, telehealth can provide immediate triage, assessment, and diagnosis of a workplace injury or illness, acceleration of diagnosis and treatment plan, increased adherence, speed of recovery, and improved outcomes.
Convenient rehabilitation – Telehealth can provide easier access to ongoing physical therapy, including home exercise programs. It can also allow an injured worker’s progress to be remotely monitored effectively and conveniently, while providing updates to physicians and employers.
Language and location accommodations – Workers in rural locations with limited access to hospitals or acute care centers often travel long distances to meet with a qualified physician. With the availability of telehealth, essential providers can be more accessible. Additionally, translators or bilingual physicians can eliminate roadblocks to care for workers with language barriers.
Reduction in ER visits – ER visits are typically associated with lengthier wait times, which can also increase exposure to additional illnesses from other patients in a waiting room. Immediate access to telehealth can quickly triage injuries and eliminate additional travel time for an injured worker.